Introduction to Business Intelligence Systems
Business Intelligence (BI) systems encompass a set of processes, technologies, and tools that organizations use to analyze historical and current data, ultimately aiding in informed decision-making. At its core, BI transforms raw data into meaningful information that can significantly enhance an organization’s strategic and operational capabilities. This is particularly crucial in today’s fast-paced and data-driven business environment, where companies are inundated with vast amounts of data from various sources.
The primary objective of implementing a BI system is to provide decision-makers with the necessary insights to drive their organizations forward. By leveraging BI, companies can identify trends, opportunities, and potential challenges within their markets. The information gathered enables leaders to make timely and well-informed decisions, which can directly impact their organization’s success. Furthermore, BI plays a critical role in improving operational efficiency by identifying areas where resources can be optimized and costs minimized.
An important aspect of BI systems is their ability to accumulate data from diverse sources, such as customer interactions, financial records, and market research, and present it in an analytical format. This holistic view of data allows organizations to gain comprehensive insights, enhancing their understanding of various business functions. Moreover, the visualization of data through dashboards and reports often makes complex information more accessible to non-technical stakeholders, facilitating collaboration across different departments.
Ultimately, the adoption of BI systems is not just about technology; it is about cultivating a data-driven culture within an organization that encourages continuous improvement and proactive decision-making. By harnessing the power of data, businesses can achieve higher levels of performance, establish competitive advantages, and better align their strategies with market demands.
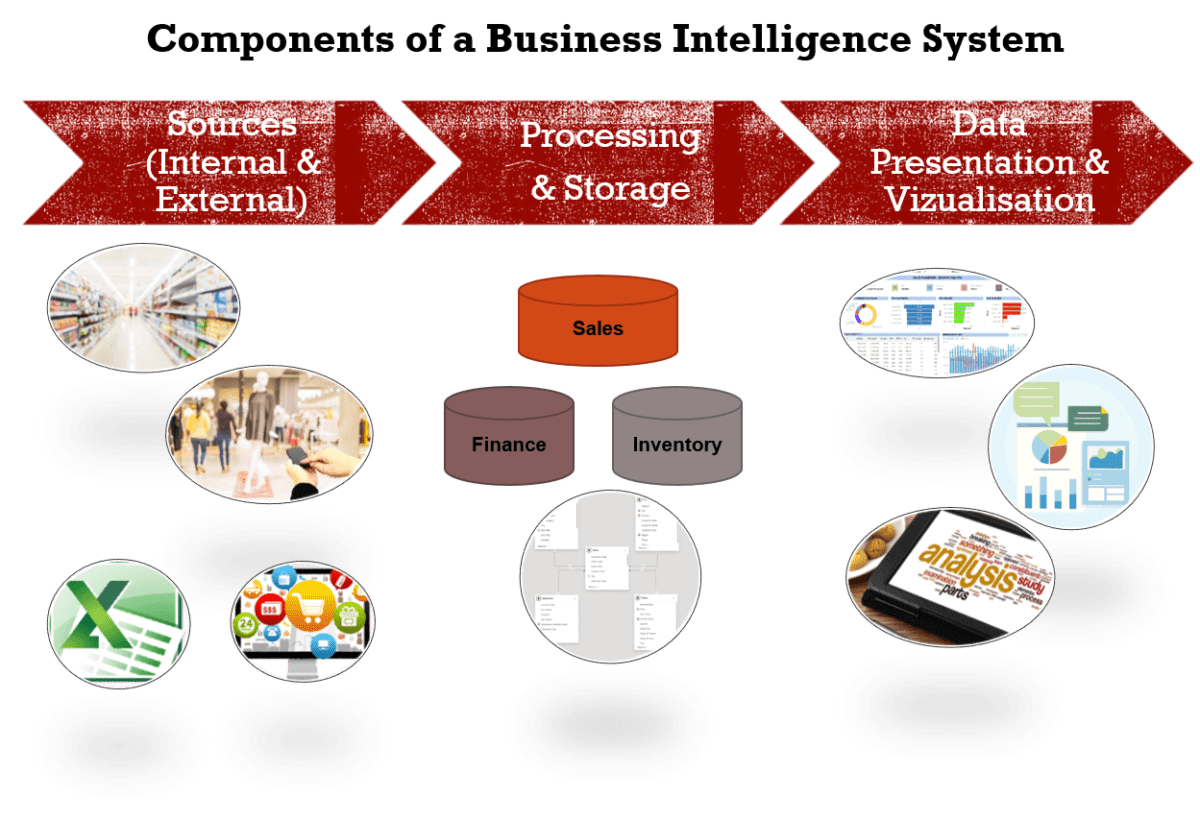
Data Sources: The Datamine for BI
Business intelligence (BI) systems heavily rely on diverse data sources to provide valuable insights that drive decision-making within organizations. These data sources can be broadly categorized into two main types: internal and external. Internal data originates from the various operations of a business, such as sales transactions, financial records, customer relationship management (CRM) systems, and supply chain activities. Each of these facets contributes to a comprehensive understanding of the organization’s performance and operational efficiencies.
For instance, sales data provides insights into customer preferences and purchasing behaviors, while financial data offers a clear picture of the company’s profitability and resource allocation. By analyzing this internal data, businesses can identify trends, understand operational strengths and weaknesses, and forecast future performance. Thus, ensuring that this data is both accurate and relevant is critical for effective analysis.
On the other hand, external data sources include information obtained from market research, social media platforms, industry reports, and demographic data. These external sources enable organizations to gain a broader perspective beyond their internal operations, allowing them to assess competitive positioning and market conditions. For example, data from social media can reveal customer sentiments and trends, while market research provides insights into consumer behavior and industry developments.
Integrating both internal and external data sources creates a robust foundation for business intelligence systems. This integration allows organizations to achieve a holistic view of their performance while remaining attuned to the ever-changing external landscape. Ultimately, the effectiveness of a BI system is determined not only by the variety of data sources it utilizes but also by the precision and relevance of the data collected. Accurate data is paramount, as it directly influences the validity of the analyses derived from the BI system, thereby informing strategic business decisions.
Data Processing and Storage: Turning Raw Data into Insights
In the realm of business intelligence, the transformation of raw data into actionable insights is a fundamental process that hinges upon effective data processing and storage. Imagine raw data as uncut gemstones—each piece holds value, but without proper handling and refinement, its true potential remains hidden. The initial step in this transformation is data cleaning. This process involves identifying and rectifying inaccuracies, removing duplicates, and filling in missing information. Just as one would polish a gemstone to reveal its brilliance, data cleaning enhances overall data quality, ensuring that decisions are informed by accurate and reliable information.
Once data is cleaned, the next phase is organizing it into structured formats. This organization can be likened to sorting files in a cabinet, where each category is easily accessible. Data can be organized through methods such as normalization or categorization, allowing users to retrieve specific information without sifting through irrelevant data. By maintaining a well-structured database, analysts can seamlessly navigate data and perform complex queries, leading to quicker insights.
Storage plays a crucial role in the business intelligence system, as it determines the accessibility and durability of data. Data can be stored in databases or data warehouses, which serve distinct purposes. A database supports day-to-day operations and transactions, while a data warehouse is optimized for analytical processing and reporting. This distinction is similar to having a bookshelf for current books versus an archive for older publications. By utilizing a data warehouse, organizations can consolidate disparate data sources, enabling comprehensive analytics and generating meaningful reports. Proper processing, organization, and storage of data are catalysts for insightful decision-making, helping businesses respond proactively to changes in their environment.
Data Visualization: Making Sense of Information
In the realm of business intelligence (BI) systems, data visualization serves as a vital component that transforms complex datasets into comprehensible visual formats. Through the use of visual tools such as charts, graphs, and dashboards, organizations are empowered to present intricate data in ways that are not only easily digestible but also visually engaging. The primary objective of data visualization is to facilitate effective communication of insights, which is essential for informed decision-making.
One of the significant benefits of utilizing data visualization within a BI framework is the ability to illustrate trends and patterns that may not be immediately apparent in raw data. For instance, a line graph depicting sales performance over time enables stakeholders to quickly recognize seasonal trends or anomalies, which can lead to timely strategic adjustments. Similarly, pie charts can provide an instant snapshot of market share distribution, helping decision-makers understand competitive positioning at a glance.
Moreover, dashboards play a crucial role by consolidating key performance indicators (KPIs) into a single, interactive interface. This allows users to monitor business health and operational efficiency in real-time. Dashboards can be customized to highlight specific areas of interest, providing a user-friendly experience that caters to various stakeholder needs, from executives to operational teams.
By portraying data visually, BI systems enhance the overall decision-making process, allowing organizations to respond swiftly to market changes and internal challenges. The clarity that visual tools provide not only aids comprehension but also encourages data-driven discussions among teams. Importantly, the elimination of technical jargon ensures that insights are accessible to a broader audience, thus empowering all stakeholders to contribute to conversations surrounding business performance effectively.
